PROJECT DESCRIPTION
INSTRUCTORS
SCHOOL SITE
LEVEL
SUBJECTS

What is Motion and how to we create and control it?
How is the science of rockets the science of your every day world?
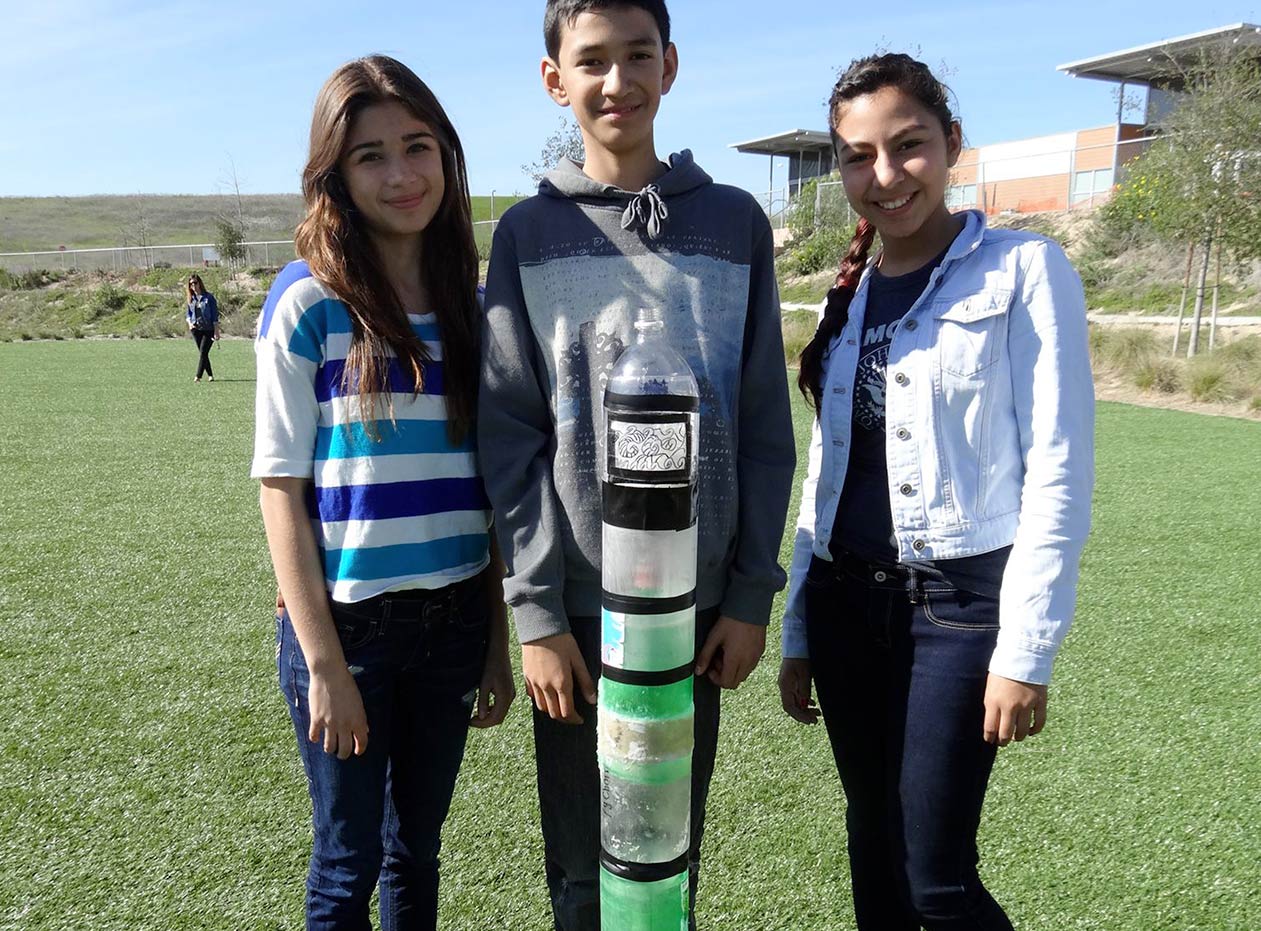
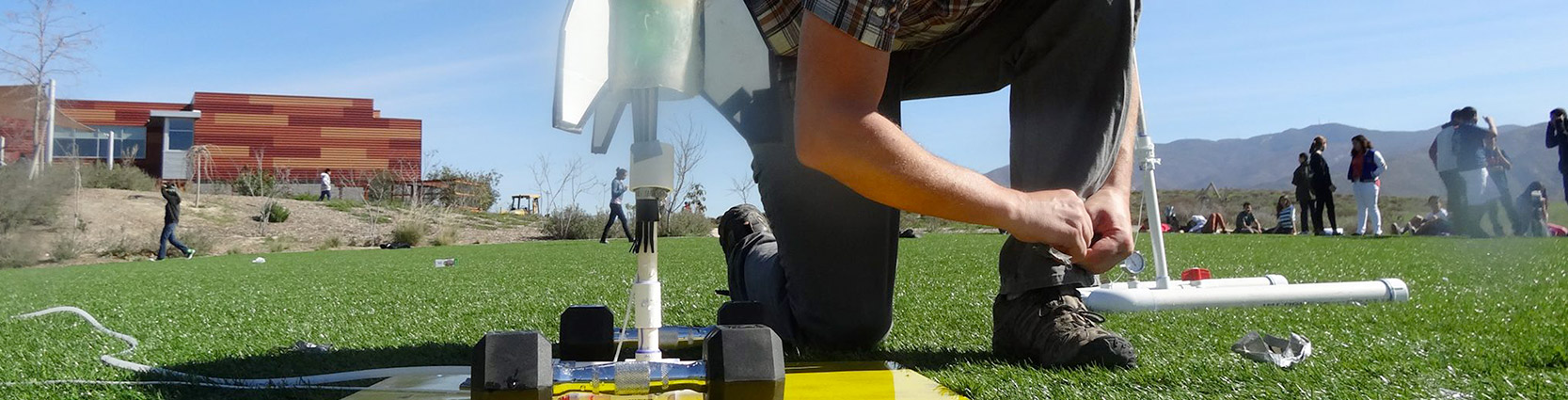
Working in teams, you will design and build rockets powered by water and pressurized air. Using what you learn about the fundamentals of force and motion, you will design and build a fully functional rocket including: payload compartment, propulsion system, recovery system and guidance system. These words may look foreign to you now, but soon you will know them as well as any rocket scientist!

| Science/Math Standard | Descriptions | Note |
| MOTION | ||
| 8PC1. | The velocity of an object is the rate of change of its position. | Khan Videos:
1) Introduction to Vectors and Scalars 2) Calculating Average Velocity or Speed Cartoon about the difference between speed and velocity. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=mDcaeO0WxBI&feature=related |
| 8PC1.a. | Students know position is defined in relation to some choice of a standard reference point and a set of reference directions. | Frames of Reference Activity:
http://www.amnh.org/learn/pd/physical_science/week2/frame_reference.html |
| 8PC1.b. | Students know that average speed is the total distance traveled divided by the total time elapsed and that the speed of an object along the path traveled can vary. | Khan Videos:
1) Introduction to Vectors and Scalars 2) Calculating Average Velocity or Speed |
| 8PC1.c | Students know how to solve problems involving distance, time, and average speed. | Khan Videos:
1)Calculating Average Velocity or Speed 2)Solving for time 3)Displacement from time and velocity |
| 8PC1.d | Students know the velocity of an object must be described by specifying both the direction and the speed of the object. | Khan Videos:
1) Introduction to Vectors and Scalars 2) Calculating Average Velocity or Speed |